Pectin is a natural edible plant polysaccharide which has been shown to be useful for the construction of delivery systems for specific pigments, flavour, fragrances, nutrition supplements, microorganisms and active pharmaceutical ingredients. Pectin hydrogels are known to be biocompatible and to exhibit very low toxicity, which are mandatory prerequisites for drug delivery application and microencapsulation. Its availability at a relatively low cost is making it one of the most popular materials for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications.
Microfluidic technology adaptation for Pectin synthesis has seen a significant growth in varied application fields. Benefits of reproducibility, real-time control and reduction of waste are few of many factors users are choosing to switch from conventional batch methods to microfluidics.
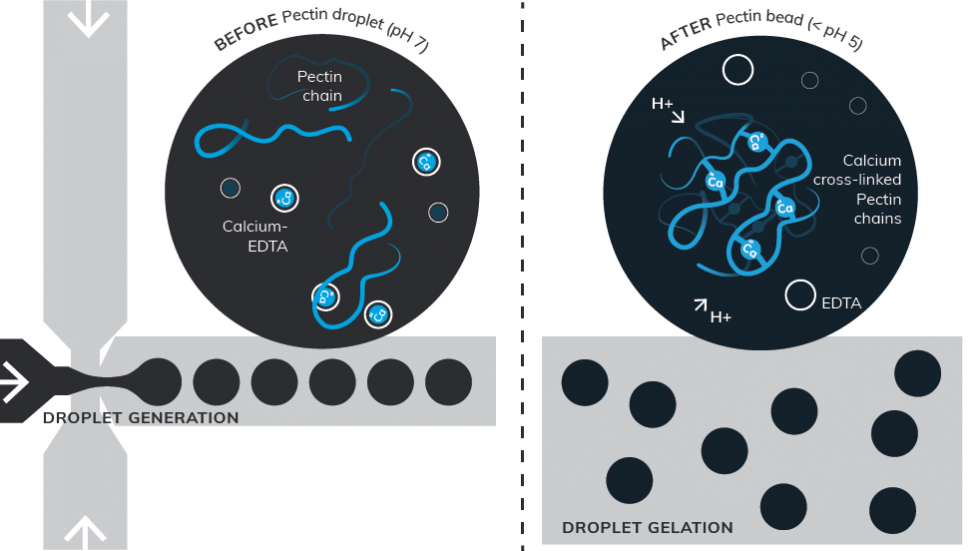
In our application note we present the Dolomite microfluidic method which is employed to produce Pectin beads. Pectin polymer and Calcium-EDTA droplets are first generated in a Large Dolomite Fluorophilic Droplet Chip using FluoSurf as continuous phase. Droplets are then collected in a gelling bath where crosslinking mechanism takes place. At low pH the H+ ions diffuse into the droplets, Calcium-EDTA complex dissociates and releases Ca2+ ions that crosslink Pectin chains giving Sodium-EDTA complex.
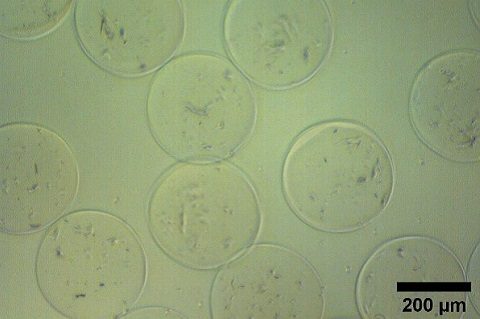
Particle dimension and shape are crucial factors affecting the release profile of the specific drug or active pharmaceutical ingredient encapsulated within the hydrogel polymer network. Uniform degradation speed and delivery time are ideal conditions in pharmaceutical and nanomedicine applications. These can be only achieved with uniform monodisperse particle systems where all particles have the same morphological and physiochemical properties.
Microfluidic technology offers the possibility to generate uniform particles characterized by a narrow size distribution, also enabling users to tune the particle dimension by simply adjusting the flow ratio between reagents. Compared to conventional bulk methods, microfluidic‐assisted particle production shows significant advantages, such as narrower particle size distribution, higher reproducibility, improved encapsulation efficiency, and enhanced scaling‐up potency.
Droplet-based microfluidic systems have shown exceptional advantages for the synthesis of monomer- or polymer-containing droplets inside which the hydrogel structures can be formed using various chemical methods. By precisely controlling the formation of the bead, we can produce alginate particles with well-defined sizes, shapes and morphologies.
The schematics below showcases the flow focusing microfluidic method example from our application note. The before and after processes of alginate crosslinking using acetic acid in the collection phase and how during the droplet gelation the Calcium-EDTA complex dissociates and releases Ca2+ ions to crosslink alginate chains.
Dolomite’s Single Emulsion Systems are the perfect solution for this application as they utilize microfluidic methods to directly generate monodisperse droplets or emulsions, eliminating the need for further processing. They can be used to generate droplets ranging in size from 2 to 200 µm, resulting in formulations such as water in oil (w/o) or oil in water (o/w) emulsions.
Methodology for generation of monodisperse pectin gel beads in sizes ranging from 65 to 305 µm using microfluidic flow focusing method.

Read about how scientists employed an in situ microfluidic synthesis method combined with settling collection, which was proven to provide an efficient approach for the preparation of soft, monodisperse hydrogel microspheres.

Read about how the scientists from the Polish Academy of Sciences approached formulation of pectin microbeads using microfluidics.

Explore the methodology for generating monodisperse polyacrylamide beads in sizes ranging from 20 to 220 µm.