The production of double emulsions is a rapidly growing area of interest in applications as diverse as drug delivery, cosmetics and food production. Many commercially successful products contain double emulsion formulations, including paints and coatings, salad dressings, and drugs.
Double emulsions consist of a droplet encapsulated within a larger droplet dispersed in a bulk liquid.
Compared to traditional batch methods of double emulsion formation, microfluidics offers a more time and cost efficient methodology.
In a single word, yes! Emulsion droplet size can impact how flavors and aromas are released from emulsions such as hot chocolate and mayonnaise. Size also impacts the speed at which drugs or agrochemicals are delivered and released, and the length of time needed between treatments.
Microfluidics provides a tool to manipulate liquids, gases, droplets, cell and particles within micro-channel geometries. The generation of droplets is a key application for microfluidics and is based on controlling the jetting to dripping transition when liquid droplets are pushed into a carrier fluid via a specific chip geometry. The droplets are stabilized using surfactants to avoid coagulation and separation.
Among its various advantages, microfluidic technology has the ability to create three-dimensional flow patterns that achieve precise control over immiscible and miscible fluid mixing.
The microfluidic generation of double emulsions requires the droplet forming flow channels to have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties on separate surface sections. Depending on their arrangement they can be used to generate either water-oil-water (w/o/w) or oil-water-oil (o/w/o) droplet emulsions.
Our microfluidic systems ensure droplet monodispersity and minimal wastage along with an effortless testing environment that provides straightforward scale-up ability.
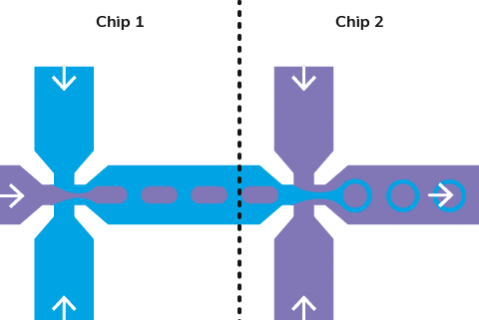
To generate precise double emulsions, users can choose from two main microfluidic techniques:
Dolomite’s Double Emulsion System is an exceptional solution for this application as it adapts varied microfluidic methods to generate monodisperse droplets, capsules, foams and emulsions, offering precise product characteristics reproducibility and effortless scale-up.

Read about our customer’s story and how our expertise assisted them with generation of w/o/w double encapsulated emulsions, using a Double Emulsion System.

Read about how our user applied the methodology to research the cytoskeletal protein expression and its association within the hydrophobic membrane of artificial cell models.

Read about how users produced double emulsions with an outer droplet size from 100 to 40 μm to perform pulsed-field gradient self-diffusion NMR experiments.